R&D, Production, Sales and Solutions of Sensing Products
A pressure sensor is a crucial device used to measure pressure in gases or liquids. It converts physical pressure into an electrical signal that can be easily measured and monitored. Pressure sensors are indispensable in a wide range of industrial, automotive, aerospace, medical, and environmental applications. They ensure safety, process control, and operational efficiency across many sectors.
- High accuracy and repeatability
- Wide pressure range
- Robust and corrosion-resistant materials
- Compact and lightweight design
- Analog and digital output options
- Overpressure protection
- Long-term stability and low drift
- Easy integration with control systems
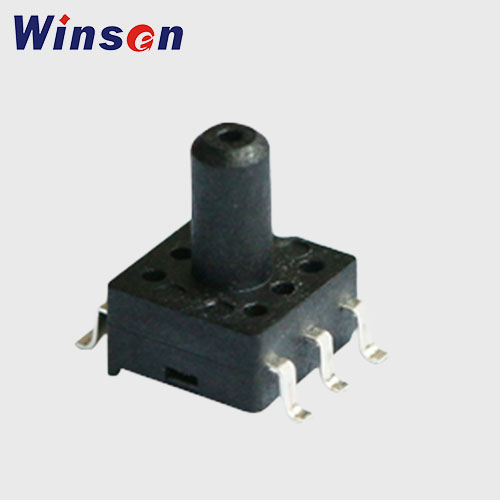
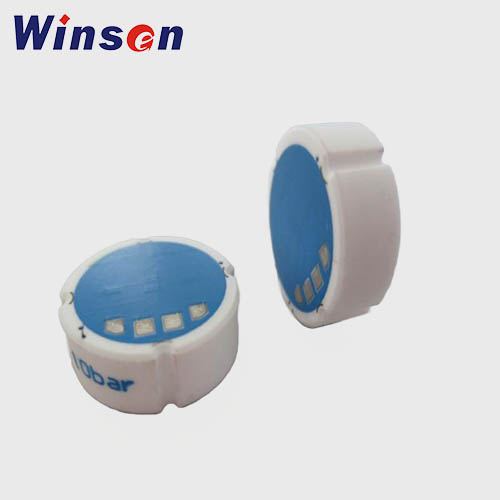









Pressure Sensors Sales
At Winsen, we offer a comprehensive range of precision-engineered pressure sensors tailored to meet various measurement requirements, including absolute, gauge, and differential pressure types. Our sensors provide reliable performance in harsh environments, making them ideal for both standard and highly specialized use cases.
Diffused Silicon Pressure Sensor
Ceramic Pressure Sensor
Plastic Sealed Pressure Sensor
Diffused Silicon Pressure Transmitter
Ceramic Pressure Transmitter
Glass Micro-Fusing Pressure Transmitter
Pressure Sensor and Transmitter Comparison Overview
| Category | Model | Power Supply / Output | Detection Range | Accuracy / Nonlinearity | Pressure Reference | Operating Temperature | Shell Material | Remarks |
| Diffused Silicon Pressure Sensor | WPAK70 | 1.5mA / mV | -100kPa ~ 0 ~ 10kPa…10MPa | ≤±0.3%FS | Gauge / Absolute / Sealed Gauge | -40℃ ~ 120℃ | – | High versatility, compact design |
| WPAK69 | 1.5mA / mV | -100kPa ~ 0 ~ 10kPa…10MPa | ≤±0.3%FS | Gauge / Absolute / Sealed Gauge | -40℃ ~ 120℃ | – | Similar to WPAK70 | |
| WPAK68 | 1.5mA / mV | -100kPa ~ 0 ~ 10kPa…100MPa | ≤±0.3%FS | Gauge / Absolute / Sealed Gauge | -40℃ ~ 120℃ | – | Extended range version | |
| WPAK67 | 1.5mA / mV | 0 ~ 10kPa…2.5MPa | ≤±0.3%FS | Differential Pressure | -40℃ ~ 120℃ | – | For differential applications | |
| WPAK66 | 1.5mA or 10V / mV | 6MPa…60MPa | ≤±0.3%FS | Sealed Gauge | -40℃ ~ 120℃ | – | Sealed design for higher ranges | |
| WPAK65 | 1.5mA or 10V / mV | -100kPa ~ 0 ~ 10kPa…16MPa | ≤±0.3%FS | Gauge / Absolute / Sealed Gauge | -40℃ ~ 120℃ | – | General-purpose sensor | |
| WPAK64 | 1.5mA or 10V / mV | -100kPa ~ 0 ~ 10kPa…25MPa | ≤±0.3%FS | Gauge / Absolute / Sealed Gauge | -40℃ ~ 120℃ | – | Moderate range coverage | |
| WPAK63J | 1.5mA / mV | -100kPa ~ 0 ~ 10kPa…100MPa | ≤±0.3%FS | Gauge / Absolute / Sealed Gauge | -40℃ ~ 120℃ | – | J-type version for special mounting | |
| WPAK63 | 1.5mA or 10V / mV | -100kPa ~ 0 ~ 10kPa…100MPa | ≤±0.3%FS | Gauge / Absolute / Sealed Gauge | -40℃ ~ 120℃ | – | Versatile with wide range | |
| Ceramic Pressure Sensor | WPAH01 | 2–20V / mV | 0 ~ 200kPa…40MPa | ≤±0.3%FS | – | -40℃ ~ 125℃ | – | High chemical resistance |
| Plastic Sealed Pressure Sensor | WPAS12 | Digital and analog | 15–115kPa | – | – | -40℃ ~ 125℃ | – | Cost-effective, compact |
| WPAS02 | Digital and analog | 10kPa ~ 100kPa | – | – | -20℃ ~ 80℃ | – | Basic sensor for air/gas | |
| WPAS01 | Digital and analog | 10kPa ~ 100kPa | – | – | -40℃ ~ 125℃ | – | Robust high-temp tolerance | |
| Diffused Silicon Pressure Transmitter | WPCK81 | 4–20mA, RS485 | 0 ~ 1m…200mH₂O | ±0.5%FS / ±1%FS | Gauge Pressure | – | Stainless steel | For deep-level and tank level measurements |
| WPCK62 | 4–20mA (Optional) | 0 ~ 35kPa…25MPa | ±0.5%FS | Gauge / Absolute / Sealed Gauge | – | Stainless steel | Widely compatible, thread options | |
| WPCK08 | 4–20mA, RS485 | 0 ~ 200mH₂O | ±0.5%FS | Gauge Pressure | – | Stainless steel | Explosion-proof version | |
| WPCK07 | 4–20mA, 0.5–4.5V, 0–5V, 1–5V, 0–10V, 1–10V | -100kPa ~ 0 ~ 10kPa…100MPa | ±0.5%FS | Gauge / Absolute / Sealed Gauge | – | Stainless steel | Full-range output types | |
| WPCK05 | 0.5–4.5V, 0–5V, 1–5V, 0–10V, 1–10V | -100kPa ~ 0 ~ 10kPa…100MPa | ±0.5%FS | Gauge / Absolute / Sealed Gauge | – | Stainless steel | Voltage output options | |
| WPCK03 | I²C, 4–20mA, 0.5–4.5V and more | -100kPa ~ 0 ~ 10kPa…100MPa | ±0.2%FS, ±0.5%FS (custom) | Gauge / Absolute / Sealed Gauge | – | Stainless steel | Flexible signal types, high accuracy | |
| Ceramic Pressure Transmitter | WPCH04 | 0.5–4.5V (Customizable) | 0.2MPa…40MPa | 0.1%FS (Default) | – | – | Stainless steel | High precision ceramic core |
| WPCH01 | 4–20mA, 0/1–5/10V, 0.5–4.5V | 0.2–5MPa | 0.1% ~ 5.0%FS (Default 2.0%) | – | – | Stainless steel | Customizable, versatile outputs | |
| WPBH01 | Proportional voltage (0.5–4.5V) | 2–400 bar (Customizable) | 0.5%, 1%, 2% (Default), 3% | – | – | Stainless steel | Broad pressure range | |
| Glass Micro-Fusing Transmitter | WPCK89 | Digital and analog | 0 ~ 100 / 150 / 250 / 500 psig | ±1%FS | – | – | Stainless steel | Extremely robust and thermally stable |
Applications of Pressure Sensors

Industrial Automation
Used to monitor and control pressure in pneumatic and hydraulic systems, pressure vessels, and manufacturing lines.

Automotive Industry
Employed in tire pressure monitoring systems (TPMS), engine management systems, and fuel systems.

Medical Equipment
Vital in devices like ventilators, anesthesia machines, and blood pressure monitors for precise pressure readings.

HVAC and Environmental Systems
Monitors airflow, duct pressure, and refrigerant pressures to maintain optimal building conditions.

Oil and Gas
Used in wellhead monitoring, pipeline control, and offshore platform instrumentation.

Consumer Electronics
Found in smartphones, wearables, and cameras for functions like altitude detection and waterproofing.
Why Global Clients Choose Us?
The company consistently adheres to the quality policy of “Fine Craftsmanship, Scientific Innovation, Pursuit of Excellence, and Value-Added Service.” By formulating production process control plans and work instructions, it has established a standardized, accountable, and regulated process management system. Additionally, the company has independently developed an MES production management system, enabling comprehensive and visual management across the entire workflow.

30+ YEARS OF EXPERIENCE
R&D, manufacture and sales of sensors and sensing solutions.
QUALITY GUARANTEE CONTINOUS IMPROVEMENT
Complete and rigid process flow control, coupled with significant improvements.


INTERNATIONAL MARKET
Deliver sensing products to more than 100 countries and regions.
STABLE SUPPLY CHAIN RELIABLE PRODUCTION
Core components not subject to constraints, advanced equipments for manufaturing and test.


R&D STRENGTH TECHNOLOGY INNOVATION
200+ patents, 180+ R&D team members, self-built labs for continous innovation.
ONE-STOP SERVICE
Professional consultation, fast delivery, 24 hours after-sales support.

Leading the Industry, Innovative & Controllable Technology
With robust R&D capabilities, we maintain sustained input in R&D and unwavering commitment to technological innovation. This not only ensures that we remain at the forefront of industry but also drives continuous innovation, leading the future trend of the sensing industry.

10% R&D Input
The average annual R&D input exceeds 10% of the annual revenue.
5+ R&D Layout
With Zhengzhou headquarters as the core, a nationwide R&D and innovation system is being established, encompassing cities of Shanghai, Wuhan, Shenzhen, and Taiyuan.
180+ R&D Team
There are over 180 R&D personnel, including more than 10 with doctoral degrees and over 50 with master's degrees, who have an average of more than 8 years of experience in sensor development.
20+ Experiment Types
Gas-related, Climatic Environment, EMC, Electrical Performance, Mechanical Performance, etc.
10+ Advanced Laboratories
CNAS Laboratory, MEMS Laboratory, UL Laboratory, Nanocomposite Materials Laboratory, etc.
400+ sets Leading R&D Equipment
Cube Storage, Die Bonder, Lithography Machine, Coating Machine, SMT Placement Machine, Automatic Probe Station, etc.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Pressure Sensors
1. What is a pressure sensor?
A pressure sensor is a device that detects and converts physical pressure into an electrical signal. It is used to monitor and control pressure in gases or liquids, commonly applied in industrial, automotive, HVAC, and medical systems.
2. What are the main types of pressure sensors?
The most common types include:
Diffused Silicon Pressure Sensors
Ceramic Pressure Sensors
Plastic Sealed Pressure Sensors
Pressure Transmitters (Diffused Silicon, Ceramic, Glass Micro-Fusing)
Each type has its specific advantages in terms of durability, accuracy, and application environment.
3. What is the difference between a pressure sensor and a pressure transmitter?
A pressure sensor typically outputs a raw signal (e.g., mV), while a pressure transmitter amplifies and conditions the signal, often outputting a standard format like 4–20mA or 0–10V. Transmitters are better suited for long-distance signal transmission and industrial environments.
4. What is meant by gauge, absolute, and differential pressure?
Gauge pressure is measured relative to atmospheric pressure.
Absolute pressure is measured relative to a perfect vacuum.
Differential pressure measures the difference between two separate pressures.
5. What is the typical accuracy of a pressure sensor?
Accuracy varies by model and application. Most industrial pressure sensors offer accuracy from ±0.1%FS to ±1%FS. High-precision versions may go below ±0.1%FS.
6. How do I choose the right pressure sensor for my application?
Key factors to consider include:
Required pressure range
Type of pressure (gauge, absolute, differential)
Output signal (analog, digital, 4–20mA, etc.)
Accuracy requirements
Environmental conditions (temperature, humidity, media compatibility)
7. Can pressure sensors work with corrosive or high-temperature media?
Yes, but you must select the right sensor material. Ceramic and stainless steel sensors often handle corrosive fluids well. For high temperatures, sensors with extended operating temperature ranges (up to 125°C or higher) are preferred.
8. What is the typical output of a pressure sensor?
It can be:
Analog: mV, 0.5–4.5V, 0–5V, 0–10V, etc.
Current loop: 4–20mA
Digital: I²C, RS485, SPI
Transmitters usually provide conditioned and standardized outputs.
9. How do I install a pressure sensor?
Most sensors have threaded process connections (e.g., G1/4″, NPT). Ensure proper sealing (using PTFE tape or gaskets), avoid over-torquing, and mount them according to manufacturer instructions to avoid signal drift or mechanical damage.
10. What are typical applications of pressure sensors?
Pressure sensors are widely used in:
Industrial automation
Water level and pump control
HVAC systems
Automotive systems (e.g., engine, brake, and fuel monitoring)
Medical devices
Refrigeration and air conditioning systems